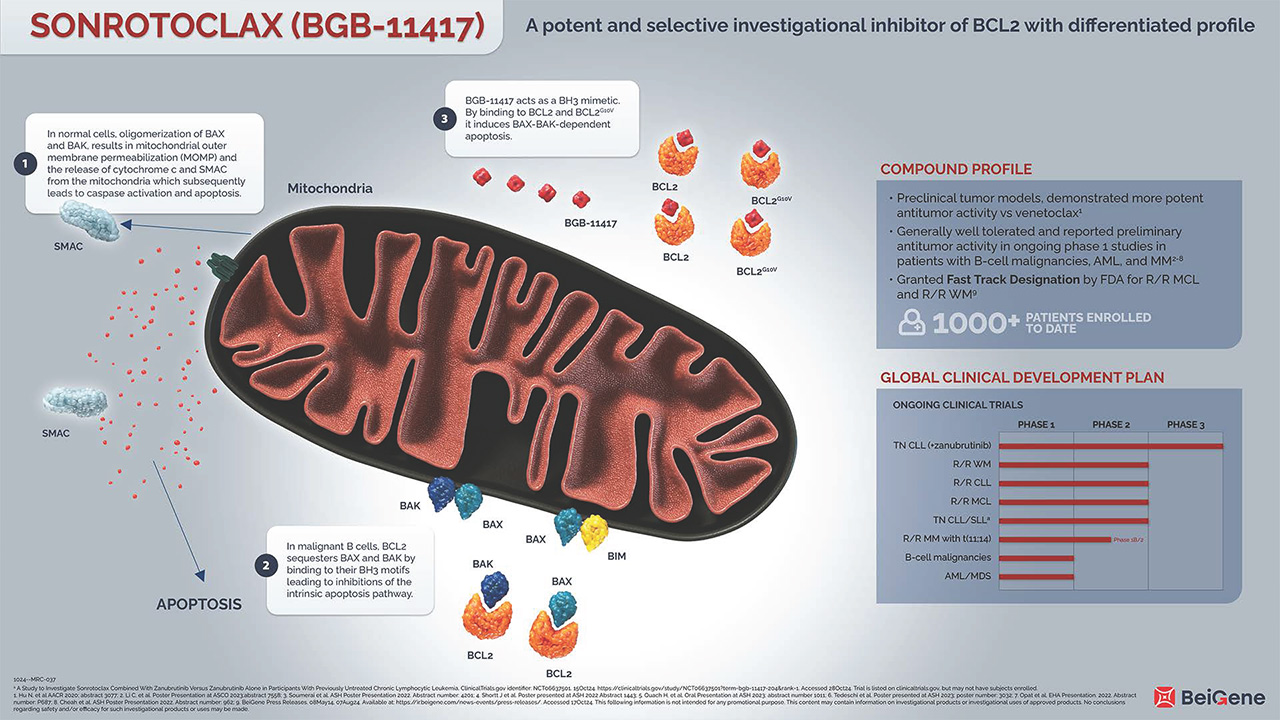
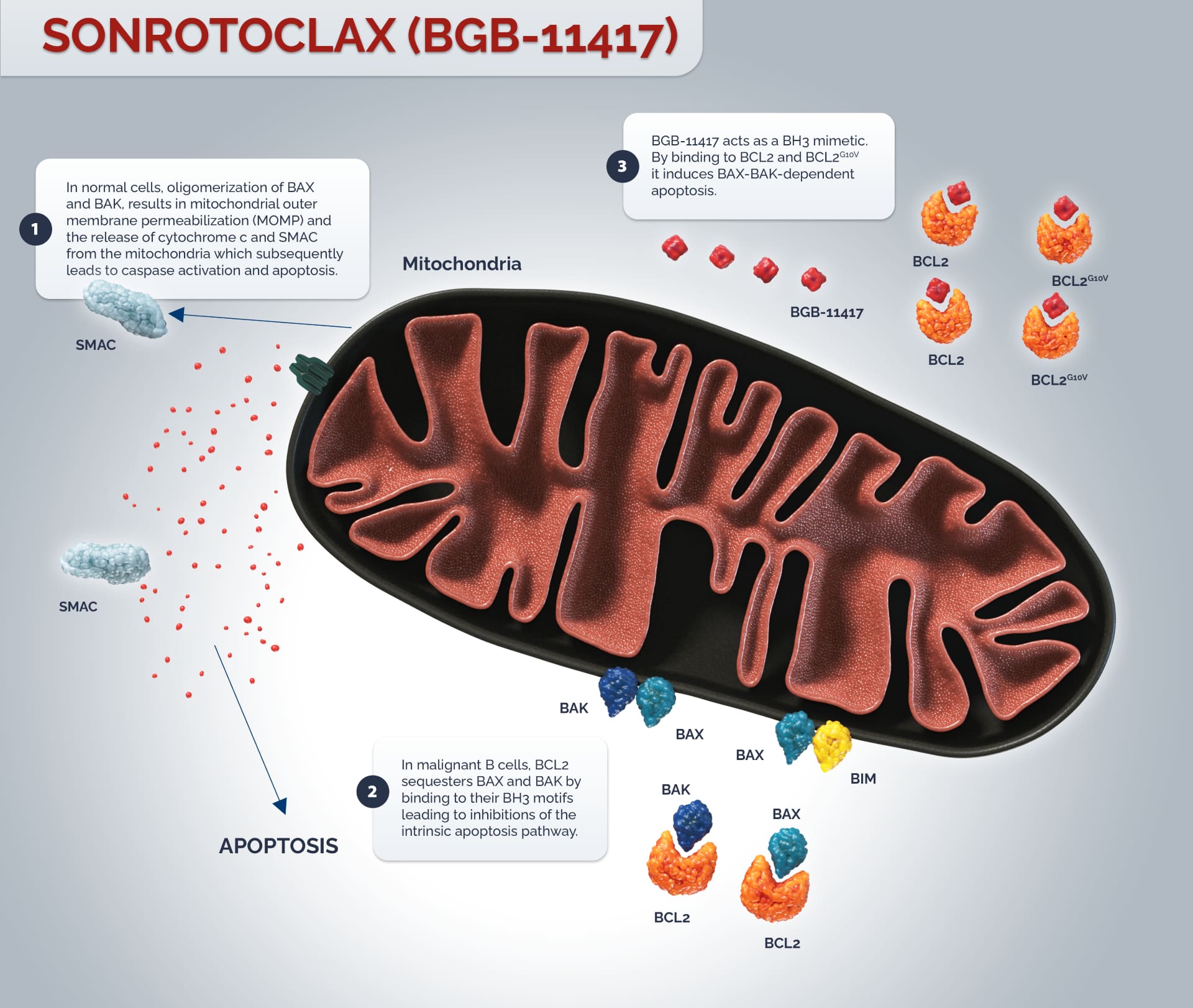
The B-cell lymphoma 2 (BCL2) gene family encodes more than 20 proteins that regulate the intrinsic apoptosis pathway, and are fundamental to the balance between cell survival and cell death.1
Acquiring resistance to apoptosis is a highly regulated process, characteristic of both hematologic malignancies and solid tumors.1,2 Anti-apoptotic BCL2 has been shown to promote malignant cell survival by attenuating apoptosis. The dysregulation of BCL2 results in overexpression of the anti-apoptotic protein BCL2 which alters the balance of pro-apoptotic members of the BCL2 family. In normal cells, cell death signals trigger BID and BIM to activate BAX and BAK. Oligomerization of the pro-apoptotic proteins BAX and BAK, results in mitochondrial outer membrane permeabilization (MOMP), the release of cytochrome c and second mitochondria-derived activator of caspase (SMAC) from the mitochondria and the subsequent activation of caspases resulting in cell death.1
Anti-apoptotic BCL2 sequesters pro-apoptotic proteins such as BAX and BAK by binding to their BH3 motifs leading to inhibitions of the intrinsic apoptosis pathway.1
Sonrotoclax acts as a BH3 mimetic. By binding to BCL2, it induces BAX-BAK-dependent apoptosis. BCL2 is a well-validated target for B-cell malignancies. With long term treatment, recurrent mutation of G10V in BCL2 has been reported to mediate resistance to BCL2 inhibitors. In pre-clinical studies, sonrotoclax potently inhibited both wildtype and G10V-mutated BCL2.3
References
- Ashkenazi, A., Fairbrother, W. J., Leverson, J. D. & Souers, A. J. From basic apoptosis discoveries to advanced selective BCL-2 family inhibitors. Rev. Drug Discov 2017;16: 273–284.
- Montero, J. & Letai, A. Why do BCL-2 inhibitors work and where should we use them in the clinic? Cell Death Differ 2018;25:56–64.
- Hu, N. et al.Abstract 3077: Preclinical characterization of BGB-11417, a potent and selective Bcl-2 inhibitor with superior antitumor activities in haematological tumor models. Cancer Res 2020;80:3077.